Objetives
Perform an isomerization reaction of C=C double bonds in acidic medium with both microscale an miniscale methodologies.
Background
Isomerization is a chemical reaction in which a molecule is converted into one of its structural isomers, a compound with the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of atoms. Double bonds are rigid structures where interconversion between Z– and E-isomers (cis and trans) does not occur. However, in acidic media protonation of the double bond can occur, with a consequent change in hybridization.
Maleic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the formula C4H4O4. It has a cis configuration, meaning that the two carboxyl groups are on the same side of the molecule. Fumaric acid, on the other hand, has a trans configuration, with the carboxyl groups on opposite sides of the molecule. Fumaric acid has a number of important applications, including the production of polymers, pharmaceuticals, and food additives. It is also used as a food acidulant and a flavor enhancer.
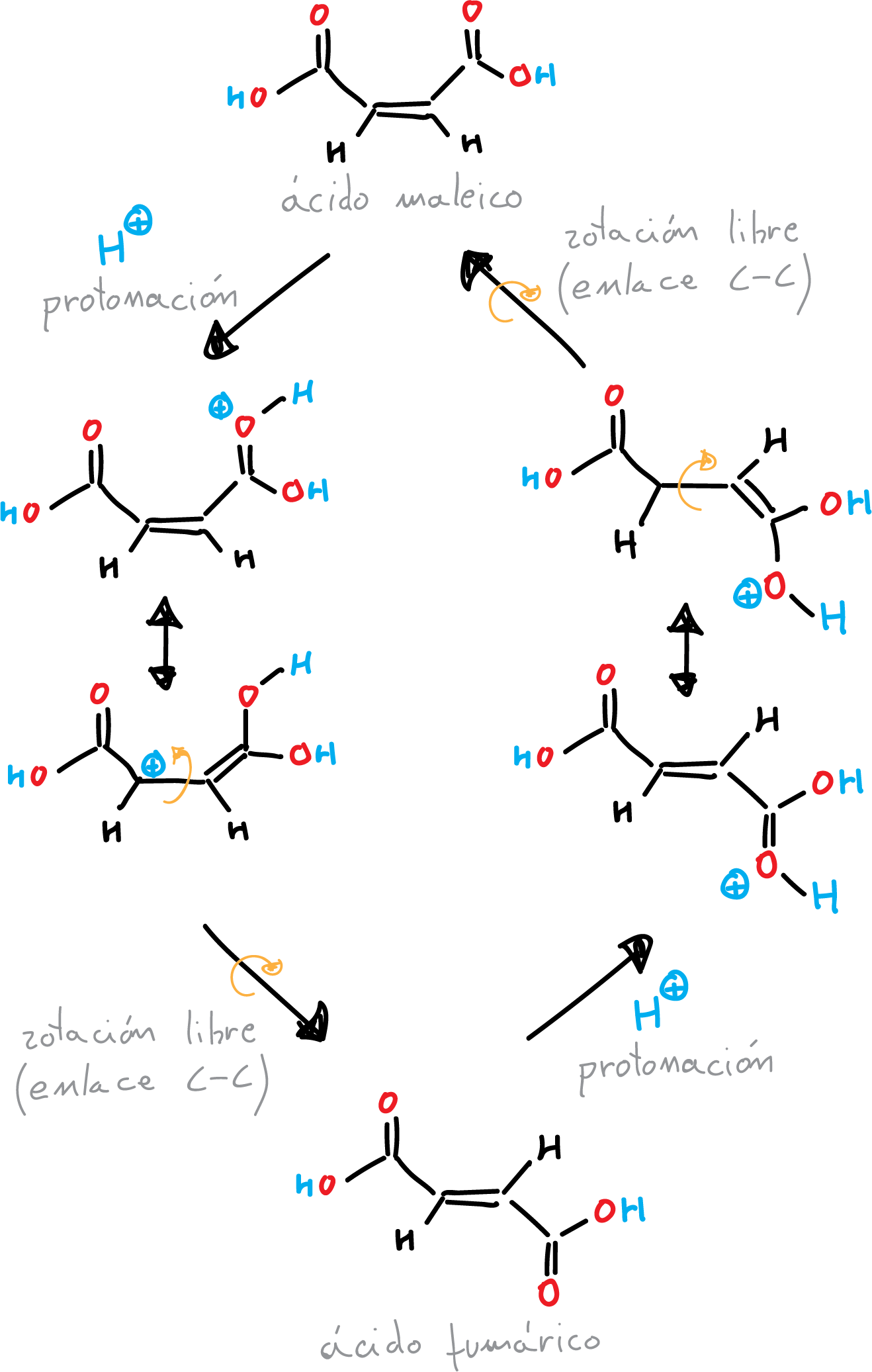
Then, (unlike the π double bond) the σ bond allows rotation of the substituents around the bond, which through an additional loss of protons regenerates the double bond again. Under equilibrium conditions, the thermodynamically most stable double bond is formed. Maleic acid is isomerized to fumaric acid by heating with acid catalysis.
The isomerization of maleic acid to fumaric acid can be achieved through several different methods. Other method is the use of a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, to convert maleic acid into its salt form. The salt is then heated to a high temperature, causing it to undergo a dehydration reaction to form fumaric acid.
Another method involves the use of a catalyst, such as palladium or platinum, to facilitate the isomerization reaction. This method is often used in industrial settings due to its high yield and efficiency.
Overall, the isomerization reaction of maleic acid into fumaric acid is an important process that allows for the production of a compound with unique properties and applications. Understanding and optimizing this reaction is crucial for the chemical and food industries.
Miniscale experimental procedure
In a round-bottom flask with magnetic stirring, place 2 g of maleic acid, 3 mL of deionized water and 2.5 mL of concentrated HCl. Attach the vial to a condenser and reflux with stirring for 20 min. A precipitate will appear and become more visible when the reaction liquid cools after the reflux time is completed.
After reaching room temperature, separate the precipitate completely by vacuum filtration. Recrystallize the solid in water; dry, weigh and determine the yield (melting point = 130 °C) and calculate the reaction yield (estimated 85 %). Verify the purity of the product by TLC using ethyl acetate / EtOH (absolute) (1: 1) as eluent.
Microscale experimental procedure
Into a conical vial provided with a spin vane, place 200 mg of maleic acid, 300 μl of deionized water, and 250 μl of concentrated HCl. Couple the vial to a condenser and reflux with stirring for 20 min. A precipitate will appear and become more visible when the reaction liquid is cooled after the reflux time is completed.
After reaching room temperature, completely separate the precipitate by vacuum filtration using a Hirsch funnel. Recrystallize the solid from water; dry, weigh, and determine the yield (m.p. = 130 ºC) and calculate the reaction yield (estimated 85%). Check purity of the product by TLC using ethyl acetate/EtOH (absolute) (1:1) as the eluent.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| Ethyl acetate | 88.11 | -84 | 77.1 | 0.902 |
| Fumaric acid | 116.07 | 287 | - | 1.635 |
| Maleic acid | 116.07 | 137-140 | 160 | 1.590 |
| EtOH | 46.07 | -114.1 | 78.5 | 0.790 |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| Ethyl acetate |   |
| Fumaric acid |  |
| Maleic acid |   |
| EtOH |  |
| HCl |   |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| Ethyl acetate | XEKOWRVHYACXOJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Fumaric acid | VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-OWOJBTEDSA-N |
| Maleic acid | VZCYOOQTPOCHFL-UPHRSURJSA-N |
| EtOH | LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Video on isomerization of maleic acid (cis) to fumaric acid (trans)
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- The photochemical isomerization of maleic to fumaric acid: an undergraduate organic chemistry experiment
Albert J. Castro, Suzanne R. Ellenberger, and James P. Sluka
Journal of Chemical Education 1983 60 (6), 521
DOI: 10.1021/ed060p521