What are isoxazoles, isothiazoles and their benzoderivatives?
Isoxazole and isothiazole are liquids of boiling point 95 and 113 ºC, respectively.

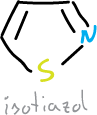
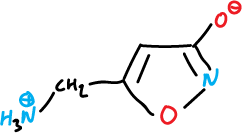
There are several natural isoxazoles with significant pharmacological activity, for example, muscimol, which is a fungus (Amanita muscaria) with psychotropic effects.
Two types of isoxazoles and benzofused isothiazoles can occur.
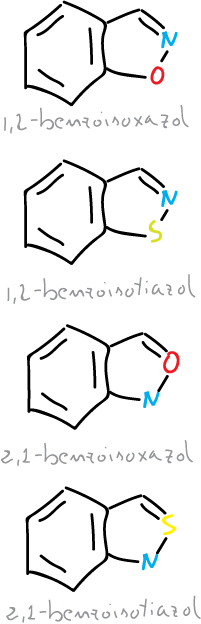
Thus, monocyclic systems and their benzoderivatives can be considered as aromatic, but they all have a weak N—X bond, which is a potential ring-opening center.
>Ring synthesis
Two main methods have been described to synthesize these rings:
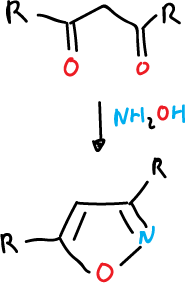
- Hydroxylamine reaction (NH2OH) with a 3-carbon atom compound, such as a 1,3-diketone or an α,β-unsaturated ketone.
This method of synthesis is not used for isothiazoles as thiohydroxylamine (NH2SH) is not available. Thus, its closest equivalent is potassium thiohydroxylamine-5-sulphonate.
It reacts with the propargylic aldehyde at the carbonyl group to give a protected thioxime intermediate that can cyclize to isothiazole.
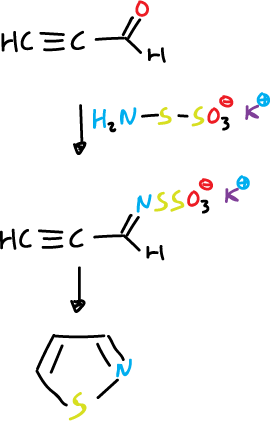
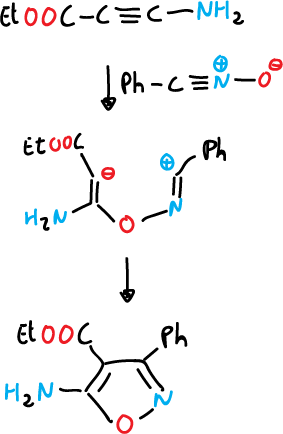
- Reaction of a nitrile oxide with an alkene (C=C) or alkyne (C≡C), generally, nitrile oxide is produced in situ.
Those with aryl substituents are generally isolable.
Two routes have been described to prepare nitrile oxide in situ and capture it.
a) From aldoximes, they are chlorinated at the α-position and the α-chloro oxime obtained produces the nitrile oxides upon reaction with a base, which is usually trimethylamine.
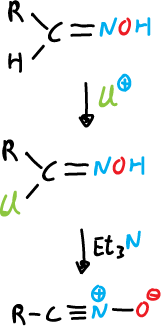
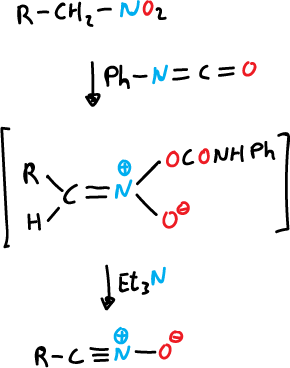
b) From nitroalkanes by treatment with phenyl isocyanate.
Once the nitrile oxide is obtained, it is reacted with alkynes.
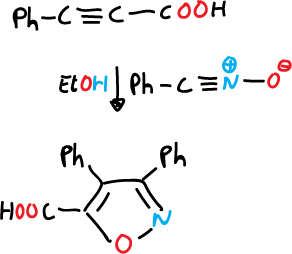
Another such reaction involving a Michael-type addition is described below.
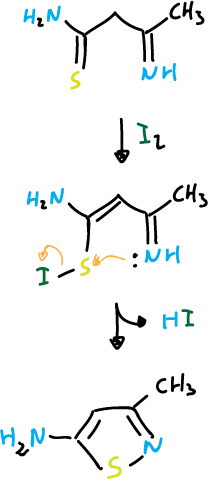
The 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions of nitrile sulfides can be used for the synthesis of isothiazoles, but it is a more limited reaction.
The most important routes of isothiazoles synthesis are based on cyclization reactions in which the N1—C5 bond can be formed. Nucleophilic attack can occur on sulfur when it presents a good leaving group. Examples of this reaction are:
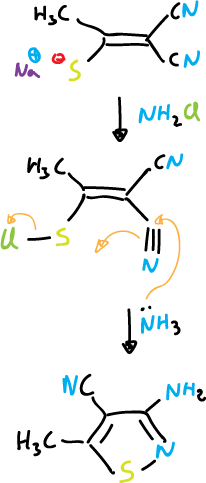
Another example would be:
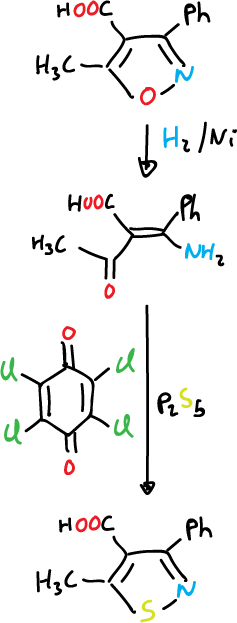
Isothiazoles can also be prepared from isoxazole by reductive opening followed by conversion to thioamide and oxidative cyclization.
Synthesis of benzofused systems
To prepare the benzofused systems of isoxazoles and isothiazoles, we start from ortho-substituted benzenes.
For isoxazoles it is done as follows:
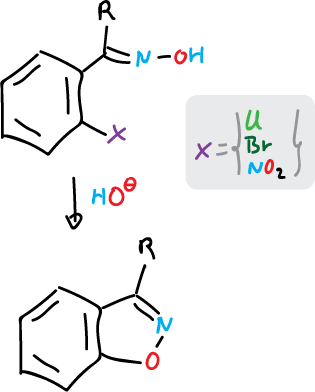
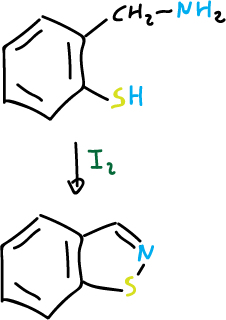
and for isothiazoles:
Also, 1,2-benzisoxazoles can be synthesized by thermolysis of 2-azidoarylketones.
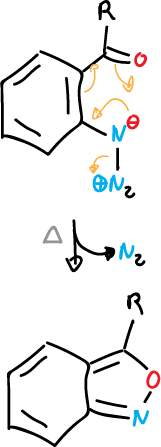
This is a general example in which aryl azides with ortho-substituent are cyclized with loss of nitrogen.
Furthermore, this reaction is carried out with 2-azidothioketones and 1,2-benzisothiazoles are obtained.
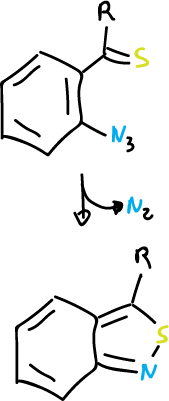
Reactions
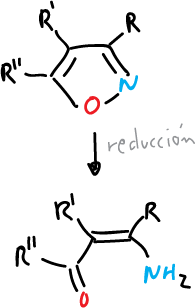
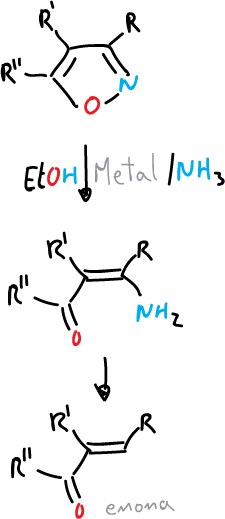
A very characteristic reaction is the easy breaking of the N—O bond of isoxazoles. The general methods of cleavage are:
- Catalytic reduction to give amino-butenones.
- Reduction with metal and ammonia to give amino-butenones and enones.
- Opening of 3-isoxazolyl anions to give α-cyanoketones.
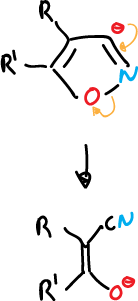
Unsubstituted isoxazoles at C3 position are readily deprotonated at C3 with hydroxyl ions. Thus, isoxazole-3-carboxylic acids are opened by heating, through the same type of mechanism.
The opening of unsubstituted isoxazolium salts at C3 position is quite easy.
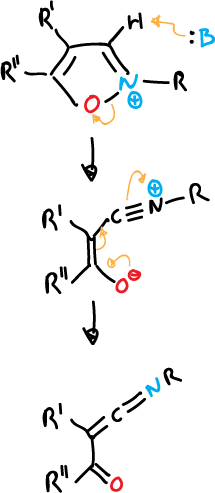
Isoxazolium salts have been used as reagents for peptide coupling.
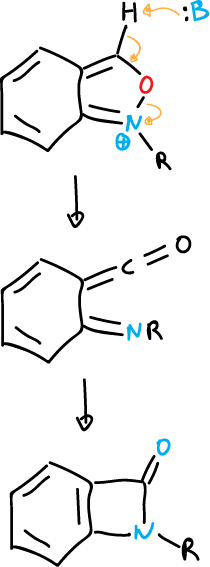
Similar ring-opening reactions occur in benzisoxazoles to yield a benzazetidinone.
Isothiazoles, too, are deprotonated at C5. In addition, when the C5 position is blocked, the 3-isothiazole anion can be formed, which undergoes the same type of opening as the isoxazole.
The sulfur atom of isothiazoles can be reductively removed by hydrogenolysis using Raney nickel.
Electrophilic substitution reactions
Both isoxazoles and isothiazoles can undergo this reaction and are preferentially substituted at the C4 carbon.
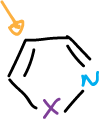
The alkyl groups at the C3 and C5 positions are slightly activated and can be deprotonated with strong bases.