What are oxadiazoles and thiadiazoles?
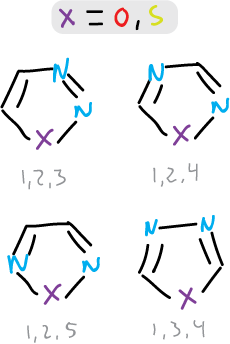
There are 4 types of isomers of these compounds.
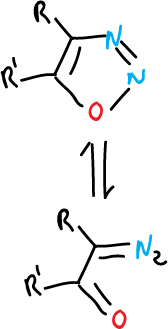
The 1,2,3-oxadiazoles exist in the open form of diazoketone (CN2O).
For the 1,2,3-thiadiazoles, however, the cyclic tautomer is the preferred structure. Also, there are the benzofused analogs of 1,2,3-thiadiazole and 1,2,5- isomers.
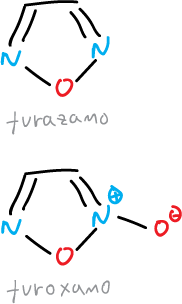
The 1,2,5-oxadiazole is also known as furazan and the 1,2,5-oxadiazole-2-oxide as furoxane.
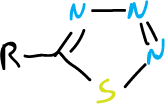
In addition, 1,2,3,4-thiatriazole derivatives have been described.
On the other hand, many biologically active derivatives of these ring systems have been synthesized and several of them form part of commercial drugs and pesticides.
Synthesis
Derivatives of these systems are obtained by cyclization reactions, although some of them can be prepared by 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition.
Some examples of this type of synthesis are shown below.
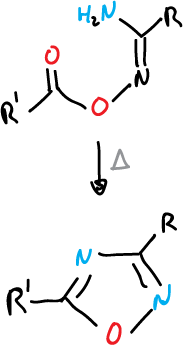
An example of formation of 1,2,5-oxadiazoles:
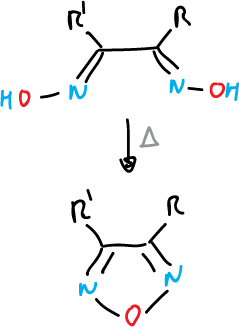
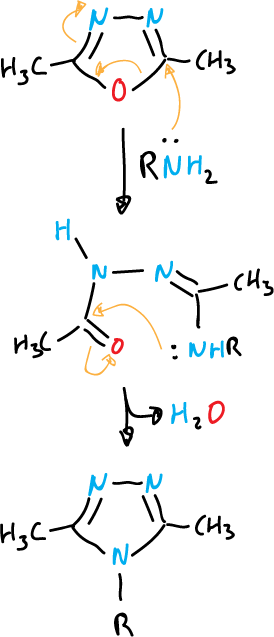
Another example, heating in an acid medium to form 1,3,4-oxadiazoles.
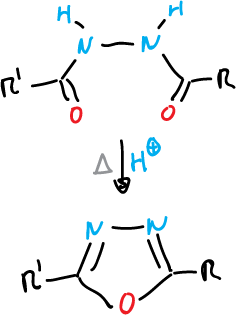
Finally, an example of the formation of 1,2,5-thiadiazoles.
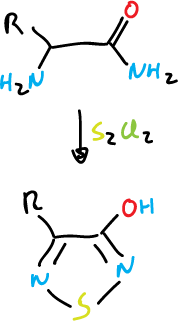
Chemical properties
The greater number of nitrogen atoms in these systems has an effect on their properties. Electrophilic substitution reactions on carbons are very rare and nucleophilic substitutions are common, especially in the case of thiadiazoles.
The 5-chloro-3-phenyl-1,2,4-thiadiazole is highly reactive towards nucleophiles. This can be attributed to the stabilization of the tetrahedral intermediate and the inductive effect of sulfur which contributes to this stabilization.
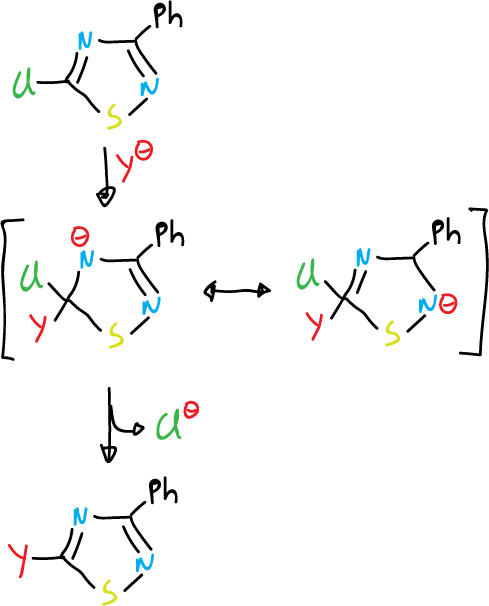
This effect is selective. For example, if we consider 3,5-dichloro-1,2,4-thiadiazole, the chlorine at C3 position is much more difficult to displace than that at C5 position.
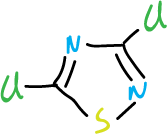
Also, other heterocycles of this group that undergo displacement are shown below:
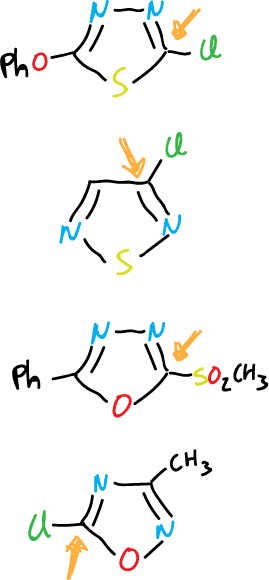
The protons of the alkyl substituents are characterized by their higher acidity.
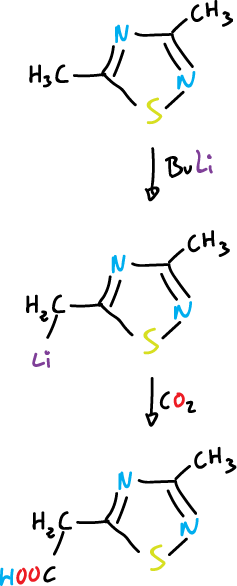
A further example of the electron-attracting nature of these systems is the properties of diazonium salts obtained by diazotization of aminothiadiazoles.
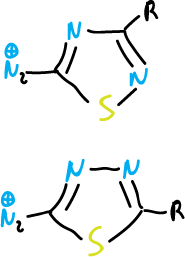
These compounds undergo copulation reactions very easily.
The azo dyes derived from these cations are of commercial importance.
Ring opening
Deprotonation of unsubstituted ring positions often leads to ring opening, as indicated in the various examples.
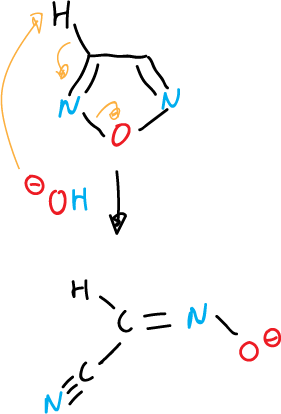
another example of fragmentation of 1,2,4-oxadiazole:
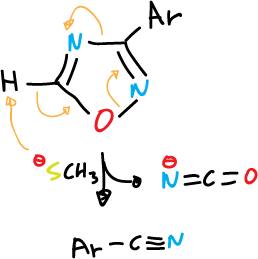
and for 1,3,4-thiadiazole fragmentation is carried out in basic medium (⊖OH):
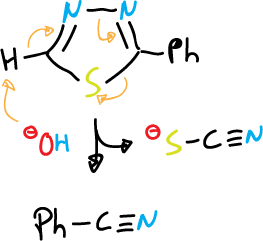
There are also other modes of ring opening, especially for oxadiazoles, by nucleophilic attack.
Many of these reactions are followed by recycling to give a heterocycle different from the original.