What are oxazoles and thiazoles?
Oxazole and thiazole are heterocycles that are closely related to furan and thiophene. The oxazole ring system is almost not found in nature and has no significant natural derivatives.
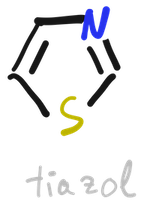
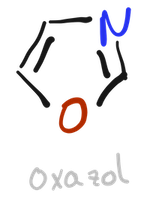
In contrast, thiazole is very common in natural products, for example, vitamin B1 (thiamine) contains a pyridine ring and a thiazole ring.
2,5-diaryl oxazoles are highly fluorescent and are used commercially as solutes in scintillation liquids and as bleaching agents.
These systems can be considered as aromatic although the oxazole bonds are more localized than those of the thiazole according to the bond length data.

As with furan, thiophene and pyrrole, here the oxygenated heterocycle is less aromatic than thiazole and imidazole and shows more diene character.
Thus, activated (electron-rich) oxazoles participate in the Diels-Alder reaction with electron-deficient dienophiles, while thiazoles rarely do so.
However, just because oxazole is less aromatic does not mean that it is unstable. Some diaryloxazoles are very heat stable and have been recovered intact after heating to 400°C.
Synthesis of oxazole and thiazole rings
Some of the basic methods are analogous to the synthesis of furans and thiophenes.
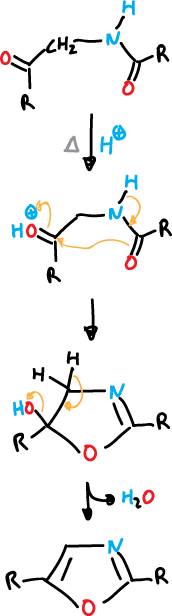
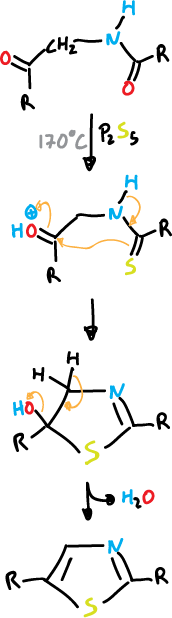
Paal-Knorr synthesis
The Paal-Knorr synthesis is based on the cyclization of 1,4-dicarbonyl compounds with appropriate functions.
For the oxazole would be
and P2S5 is used for the thiazole.
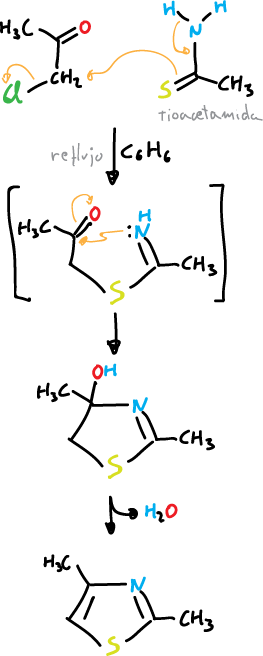
From α-halocarbonyl compounds by reacting them with the appropriate reagents.
For the thiazole the synthesis would be:
And for oxazole:
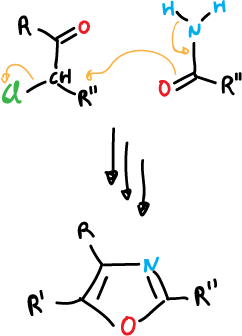
Another general procedure is by [4+2] addition reactions of the 1,3-dipolar type.
The compounds generally have an R—C≡C—R or R—C≡N triple bond, but olefins can also be used.
Generally, both of them usually have one or more electron attractors and usually different ones.
Reactions
Oxazole is a very weak base and its salts are unstable. N-alkyl oxazolium salts have been formed from various substituted oxazoles and it is possible to quaternize the thiazoles in nitrogen with various alkylating agents.
These salts can easily undergo hydrogen-deuterium exchange at C2 and in the process ylides are generated as intermediates.
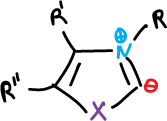
The exchange rate is higher for oxazolium salts, but thiazolium ylides are more stable due to the ability of sulfur to stabilize the carbanion.
The neutral oxazoles and thiazoles are also preferentially deprotonated at C2 by strong bases. They are also lithiated by reactions with phenyl lithium at -60 ºC.
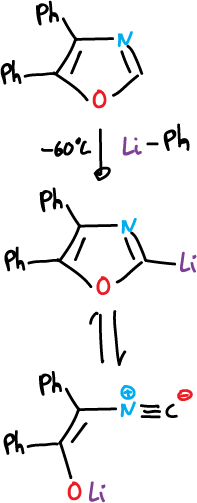
This lithiated compound is unstable and the ring is opened to give the isonitrile.
Alkyl groups in the C2 position can lose protons and the resulting anions can react with reagents.
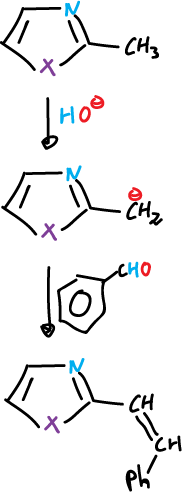
Electrophilic reagents
The entry of a nitrogen into the heterocycle decreases the ease of attack by electrophilic reagents. This deactivation is greater in those reactions that require acidic media, e.g. nitration, sulfonation and Friedel-Crafts reactions.
Electrophiles attack oxazoles and thiazoles at C5 preferentially and then at C4.
The oxazole does not readily undergo electrophilic attack unless it has electron-donating substituents. The substituents, in general, act in the same way as in benzene.
If the ring has a strongly deactivating substituent, the new substitution does not take place.
If the ideal position for substitution is occupied, the strongly activating substituents facilitate the substitution to other positions.
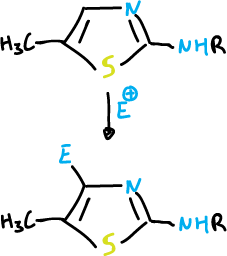
The oxazoles y thiazoles with a leaving group in the C2 position react with the nucleophiles to give displacement products.
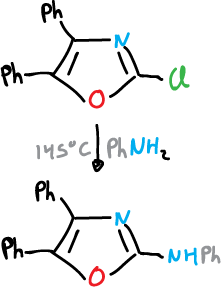
For thiazoles the reaction is as follows.
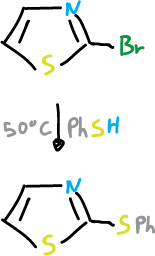
The thiazole undergoes a nucleophilic amination at the C2 position which is analogous to the Chichibabin reaction of pyridine.
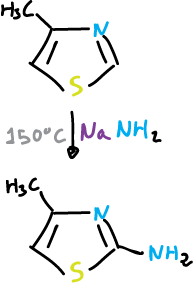
One of the most relevant reactions of oxazole is the typical diene Diels-Alder reaction. An electron donor group (ethoxyl) facilitates the reaction with dienophiles.
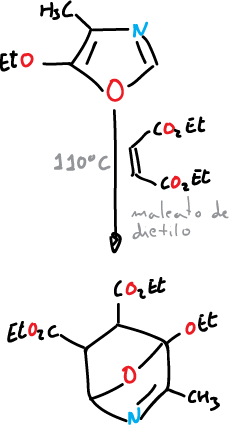
This reaction offers a good route for synthesis of, for example, pyridines.
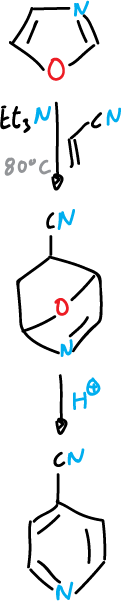
When the dienophile is acetylenic we arrive at furan.
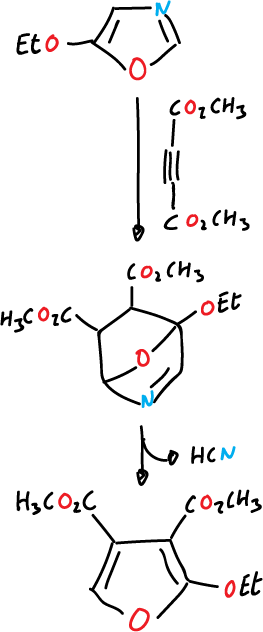
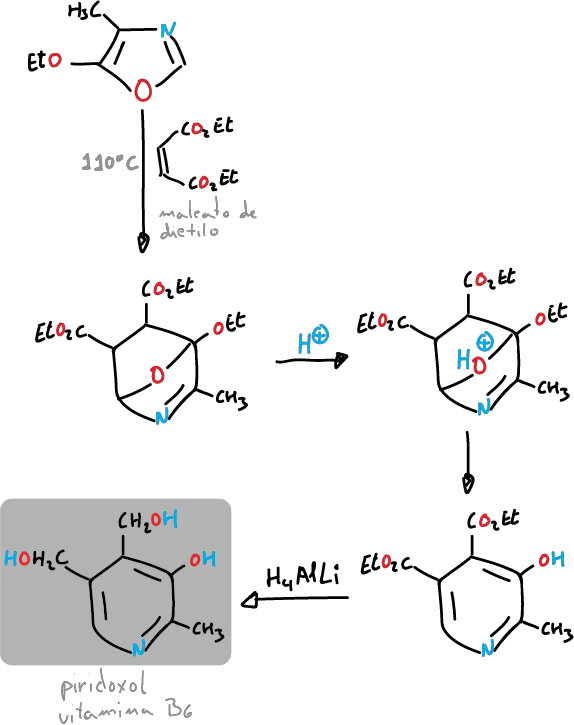
and can also be used for the synthesis of pyridoxol (vitamin B6).
Photooxygenation
Photooxygenation in oxazoles involves the addition of singlet oxygen between the C2 and C5. positions. The form of decomposition of the unstable endoperoxide depends on the solvent, but it is possible to isolate thiamides from trisubstituted oxazoles.
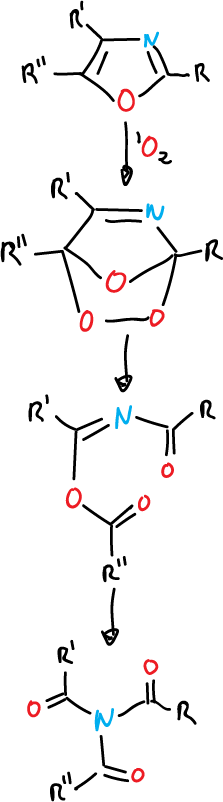
Trisubstituted thiazoles react in the same way with singlet oxygen.