Bohrium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the atomic number 107. It is a silvery-white metal that is highly radioactive and toxic. Bohrium is not found naturally on Earth and must be produced in a laboratory. Bohrium is an artificial element named after the Danish Nobel laureate physicist Niels Bohr, who made significant contributions to our understanding of the structure of atoms and the nature of radiation. This was to honor his model of the electron shell structure of atoms. Bohrium was first produced by colliding chromium atoms with bismuth atoms in a particle accelerator. Atoms of this metal are unstable. Thus, half of any sample of bohrium atoms decays in 61 seconds.
Electron configuration
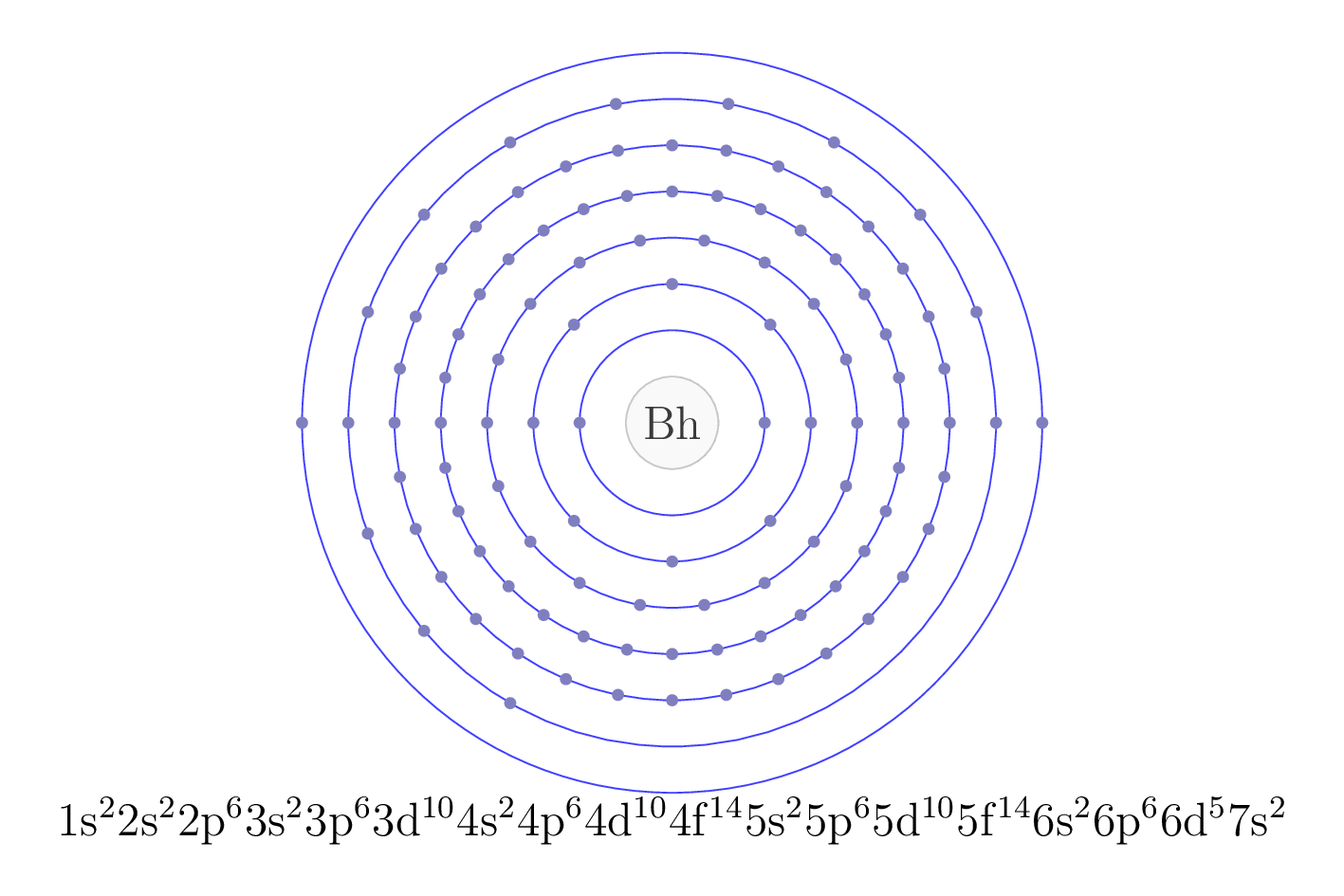
The electron configuration of an element describes the arrangement of electrons in the atoms of that element, and be used to predict its chemical properties and reactivity.
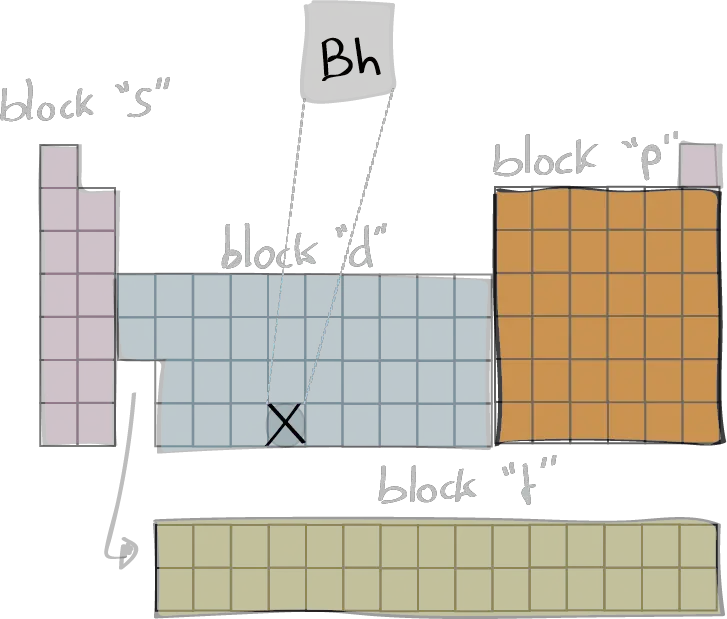
In the electron configuration notation, the letters "s", "p", "d", and "f" represent the different types of atomic orbitals, and the superscripts indicate the number of electrons in each orbital. The orbitals are filled in a specific order, starting with the lowest energy orbital and working up.
Symmary of properties (Bh)
| Atomic weight | [270] |
| Discoverer (year) | Oganessian (1981) |
| Natural form | metallic solid (-) |
| Electron configuration | [Rn] 7s2 5f 14 6d5 |
| M.p. (ºC) | |
| B.p. (ºC) | |
| Earth's crust abundance (ppm) | sintético |
| Isotope (abundance %) | |
| Density (g/cm3) | |
| vdW radius (pm) | |
| Covalent radius (pm) | 141 |
| Electronegativity (Pauling) | |
| Vaporisation enthalpy (Kj/mol) | - |
| Fusion enthalpy (kJ/mol) | - |
| Specific heat capacity (J/g·K) at 25ºC and 1 at | - |
| Thermal conductivity (W/cm·K) at 25 ºC and 1 at | - |
| Oxidation number | |
| Electronic affinity (eV) | |
| 1st Ionization energy (eV) |
Definition of terms in the previous table
- Atomic weight: The average mass of an element's atoms, typically given in atomic mass units (amu).
- Natural form: The most stable and abundant form of an element that occurs naturally in the environment.
- Electron configuration: The arrangement of electrons in an atom or molecule.
- Melting point: The temperature at which a solid substance turns into a liquid.
- Boiling point: The temperature at which a liquid substance turns into a gas.
- Earth's crust abundance (ppm): The concentration of an element in the Earth's crust, typically given in parts per million (ppm).
- Isotope (abundance %): A variant of an element that has the same number of protons in the nucleus, but a different number of neutrons. The abundance of an isotope is the percentage of the isotope in a sample of the element.
- Density (g/cm3): The mass of a substance per unit volume.
- vdW radius (pm): The radius of an atom or molecule as predicted by the van der Waals model, typically given in picometers (pm).
- Covalent radius (pm): The distance from the center of an atom to the center of another atom with which it is bonded covalently, typically given in picometers (pm).
- Electronegativity (Pauling): A measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond, based on the Pauling scale.
- Vaporisation enthalpy (kJ/mol): The amount of energy required to convert a substance from a liquid to a gas at a constant temperature.
- Fusion enthalpy (kJ/mol): The amount of energy required to convert a substance from a solid to a liquid at a constant temperature.
- Specific heat capacity (J/g·K) at 25ºC and 1 at: The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius at a constant pressure.
- Thermal conductivity (W/cm·K) at 25 ºC and 1 at: The ability of a substance to conduct heat, typically given in watts per centimeter per kelvin.
- Oxidation number: A positive or negative integer that represents the number of electrons that an atom has gained or lost in a chemical compound.
- Electronic affinity: The energy change associated with adding an electron to a neutral atom to form a negative ion.
- 1st Ionization energy: The energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from a neutral atom.