Objetives
Perform an electrophilic aromatic SEAr substitution reaction, particularly a Friedel-Craft alkylation in tert-butylbenzene.
Background
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction of aromatic rings is a C-C bond forming reaction, which often uses alkyl halides (R-X) as alkylating agents and a Lewis acid (AlCl3) as catalyst. However, this reaction has some limitations since, firstly, the primary alkyl halides undergo transposition processes under the reaction conditions and, secondly, they often generate polyalkylation products such as alkyl derivatives of benzene, which are more reactive to the Friedel-Crafts alkylation than benzene itself.
In this experiment, the alkylating agent (tert-butyl chloride) is prepared from tert-butanol and HCl (conc.) by SN1 reaction.

In the second step, tert-butyl chloride is used in a Friedel-Crafts reaction using tert-butylbenzene as substrate.
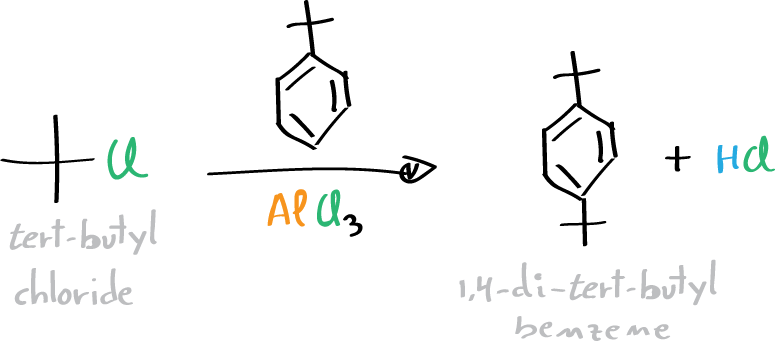
Experimental procedure
Synthesis of tert-butyl chloride by reaction SN1
Fix a metal ring inside a fume hood, place a 250 ml extraction funnel in the metal ring. Pour 25 ml of tert-butyl alcohol into the funnel. Very slowly, add 100 ml of 12 N HCl and slowly mix the two layers formed. Then shake vigorously for 2 to 3 min, continuously, sporadically opening the funnel stopcock to release the gases produced and avoid overpressure. Then shake the funnel again, this time, from time to time, for 10 min. Let the mixture stand until the two phases are clearly separated.

| DANGER! “Always work in a fume hood. Given the irritant and tear-inducing nature of tert-butyl chloride, measure the appropriate amount in the fume hood.” |
Then discard the lower (aqueous) phase and wash the upper (organic) phase with a 5 % K2CO3 solution (2 × 10 ml), opening the funnel stopcock to avoid overpressure. Then, transfer the organic phase to a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask and proceed with the drying of the solution in anhydrous Na2SO4. Remove the desiccant by gravity filtration.
Transfer the obtained solution to a dry round-bottom flask of 50 ml that is attached to the necessary components to set up a simple distillation equipment (heated with hot plate). Collect two fractions: a first fraction with the first drops of distillate; secondly, the distilled material is collected (48-54ºC) in a dry round-bottom flask (previously tared).
Discard both the first fraction and the residue remaining in the flask. Weigh the second fraction, and calculate the yield, using the obtained compound (tert-butyl chloride) to continue with the next step.
Preparation of 1,4-di-tert-butylbenzene (Friedel-Crafts alkylation)
In a 100-ml three-neck flask equipped with a thermometer, place 20 ml of tert-butyl chloride, then 10 ml of tert-butyl-benzene, and a stir bar. Weigh 1 g of AlCl3 on a substance weigher and store it immediately until use in a test tube with a stopper. Connect the flask to a washing trap with sodium bicarbonate solution (NaHCO3) to trap the HCl (gas) that emerges with the formation of CO2. Place the flask in an ice water bath to cool it to a temperature between 0 and 3 °C. Add about a quarter of the AlCl3 through the neck of the flask.
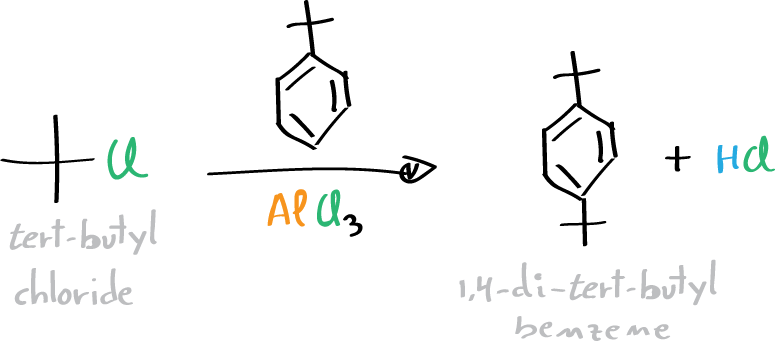
Remove the thermometer, cover and shake the flask vigorously while it is in the ice bath. After a period of about 2 min, a strong reaction occurs, releasing HCl (gas). Add the rest of the catalyst in three times at 2 min intervals. When the reaction is finished, a white solid will appear and bubbling will cease. When this occurs, disconnect the wash trap, preventing the return of the solution, and remove the flask from the ice water bath.
Allow the reaction crude to stand at room temperature for 5 min and add ice water to the reaction mixture so that when the ice melts, the crude can be easily extracted. Then transfer the contents to a separating funnel and extract with diethyl ether (2 x 20 ml).
Combine the organic extracts (upper layer) and dry over sodium sulfate in a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask. Remove the solvent under reduced pressure (rotary evaporator). The resulting oily substance can crystallize when cooled. Weigh the product and calculate the yield. Recrystallize from MeOH (20 ml MeOH per 15 g product) and cool in an ice bath until the solid separates completely.
Physico-chemical properties
This table collects data for the molecular weight (Mw), melting point (M.p.) boiling point (B.p.) and density of the reactives and compounds used in this laboratory experiment.
| Name | Mw (g/mol) | M.p. (ºC) | B.p. (ºC) | Density (g/ml) |
| 1,4-Di-tert-butylbenzene | 190.32 | 76-78 | 236 | 0.985 |
| AlCl3 | 133.34 | 100 | 120 | 2.440 |
| tert-Butyl chloride | 92.57 | -25 | 51-52 | - |
| tert-Butyl alcohol | 74.12 | 23-26 | 83 | 0.786 |
| CO2 | 44.01 | -78.5 | - | - |
| Diethyl ether | 74.12 | -116 | 34.6 | 0.71 |
| HCl | 36.46 | -30 | >100 | 1.200 |
| K2CO3 | 138.21 | 891 | - | - |
| MeOH | 32.04 | -98 | 64.7 | 0.791 |
| NaHCO3 | 84.01 | 300 | - | 2.160 |
| Na2SO4 | 142.04 | 884 | - | 2.630 |
GHS pictograms
Hazard pictograms form part of the international Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) and are collected in the followinf Table for the chemical compounds used in this experiment.
| Name | GHS |
| 1,4-Di-tert-butylbenzene |  |
| AlCl3 |  |
| tert-Butyl chloride |  |
| tert-Butyl alcohol |   |
| CO2 |  |
| Diethyl ether |   |
| HCl |   |
| K2CO3 |  |
| MeOH |    |
| NaHCO3 | Non-hazardous |
| Na2SO4 | Non-hazardous |
International Chemical Identifier
The IUPAC InChI key identifiers for the main compounds used in this experiment are provided to facilitate the nomenclature and formulation of chemical compounds and the search for information on the Internet for these compounds.
| 1,4-Di-tert-butylbenzene | OOWNNCMFKFBNOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| AlCl3 | VSCWAEJMTAWNJL-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
| tert-Butyl chloride | NBRKLOOSMBRFMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| tert-Butyl alcohol | DKGAVHZHDRPRBM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CO2 | CURLTUGMZLYLDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| Diethyl ether | RTZKZFJDLAIYFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| HCl | VEXZGXHMUGYJMC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| K2CO3 | BWHMMNNQKKPAPP-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
| MeOH | OKKJLVBELUTLKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| NaHCO3 | UIIMBOGNXHQVGW-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| Na2SO4 | PMZURENOXWZQFD-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
References
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J. A.; Calvo-Flores, F. G.; and Martínez-García, H. (2015). Experimental Organic Chemistry Laboratory Manual. Elsevier Science & Technology. ISBN: 978-0-12-803893-2
- Vogel, A.I., Furniss, B.S., Hannaford, A.J., Tatchell, A.R., and Smith, P.W.G. (1989). Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry (Vogel’s Textbook series). Longman. ISBN: 9780470214145