What is riboflavin?
Vitamin B2, or riboflavin, is part of the water-soluble B vitamin complex. The systematic name of the IUPAC is 7,8-Dimethyl-10-[(2S,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl]benzo[g]pteridine-2,4-dione.
Chemical structure
It has a general formula C17H20N4O6. It consists of a heterocyclic structure (benzene ring fused to pteridine with two carbonyl groups) called isoaloxazine and a substituent, ribitol (pentose), linked to a nitrogen.
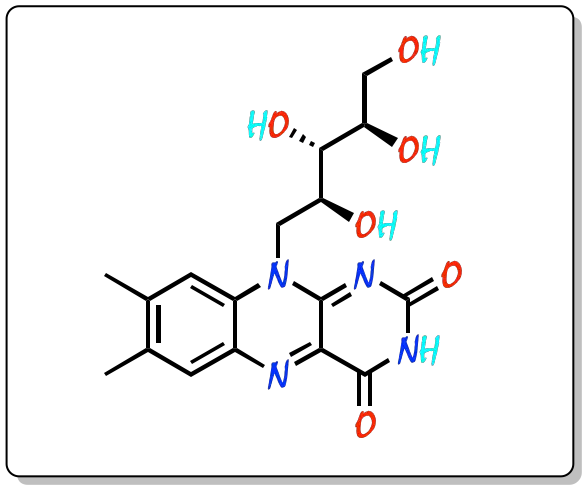 |
| 3D Structure |
Functions
It plays a major role in processing amino acids and fats, forming red blood cells, converting carbohydrates into energy, activating vitamin B6 and folic acid, and maintaining mucous membranes in the digestive tract.
Chemical properties
Industrial synthesis
Biotechnological processes are used, which employ different types of microorganisms. For example, filamentous fungi and yeasts such as Ashbya gossypii, Cándida famata and Cándida flaveri, and bacteria such as Corynebacterium ammoniagenes or Bacillus subtilis. The latter bacteria have been genetically modified to increase riboflavin production.
Food sources
Legumes, brewer’s yeast, soy products, kidney, liver, milk, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, asparagus, eggs, legumes, spinach, yogurt and meat.