What is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is made up of two fat-soluble compounds. These are vitamin D3, or cholecalciferol, and vitamin D2, or ergocalciferol. Vitamin D is a unique substance, as it is produced in the body when the skin receives solar radiation. The IUPAC systematic name for vitamin D3 is (3S,5Z,7E)-9,10-secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol and for vitamin D2 is (3S,5Z,7E,22E)-9,10-secoergosta-5,7,10(19),22-tetraen-3-ol
Chemical structure
Vitamin D3 or cholecalciferol is generated in the skin by the action of ultraviolet (UV) rays from sunlight on the compound 7-dehydrocholesterol. Subsequently, cholecalciferol is transformed by hydroxylation in the liver to 25-hydroxycholecalciferol (calcidiol) which is hydroxylated again in the kidney to form 1α-25 dihydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol) which is the active form.
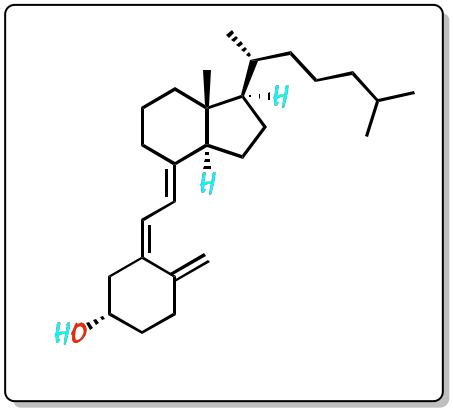 |
| 3D Structure |
Like vitamin D3, ergocalciferol (vitamin D2) is a seco-steroid (derived from a steroid that undergoes ring cleavage, in this case the B-ring). Thus, it is formed by photochemical cleavage (by the action of ultraviolet (UV) light) on ergosterol (provitamin D2).
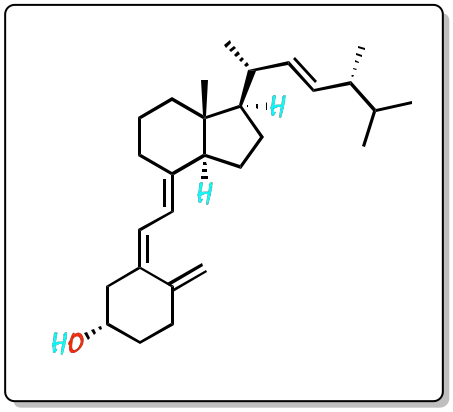 |
| 3D Structure |
Functions
Vitamin D stimulates calcium absorption and helps fight breast and colon cancer. It also helps maintain adequate blood levels of calcium and phosphorus.
Food sources
Cold-water fish, egg yolks, butter and dark green leafy vegetables. In addition, vitamin D, in the form of vitamin D2 (or ergocalciferol) is often added to milk and other foods.